Physical Properties of Metals and Non-metals
Physical Properties of Metals and Non-metals: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Metals and Non-Metals, Metals, Non-Metals, Malleability of Materials, Hardness of Materials, Ductility of Materials, Sonority of Materials, and Thermal Conductivity of Materials.
Important Questions on Physical Properties of Metals and Non-metals
Making bronze requires copper and tin ores. Why do you think that the Bronze Age coincided with increased trade between groups of people?
The metal used in building bridges is _____.
Copper is used for making
Which of these is a metal?
Why are metals good conductors of electricity?
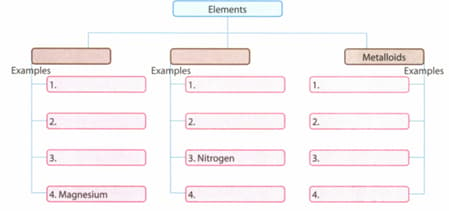
Complete the concept map.
State the differences between malleability and ductility.
Most non-metals are good conductors of electricity.
Sodium and potassium can be cut with a knife.
Bromine is a non-metal that is liquid at room temperature.
All the metals are non-conductors of electricity.
How can you examine that metals conduct electricity? Explain with the help of an activity?
Give a comparative account between metals and non-metals with examples.
Which of the following is malleable?
Name the following:
A non-metal that is liquid at room temperature: _____.
Name the following:
The hardest non-metal: _____.
_____ is the only metal found in the liquid state at room temperature.
Identify the electric conductivity of materials with an experiment.
Most of the human body is made up of water . It isn’t surprising that the majority of a human body’s mass is oxygen. Carbon, the basic unit of organic molecules is the second. 99% of the mass of the human body is made up of just six elements. Oxygen , carbon , hydrogen , Nitrogen , calcium , phosphorus . Can we decide whether our body is metal or non-metal?
How will you close the circuit using sulphur, carbon or iodine? They may be in powder form. Try to tightly pack the powder in a straw and use it. Think of other ways.
